Tank T-72 facing the camera under a cloudy sky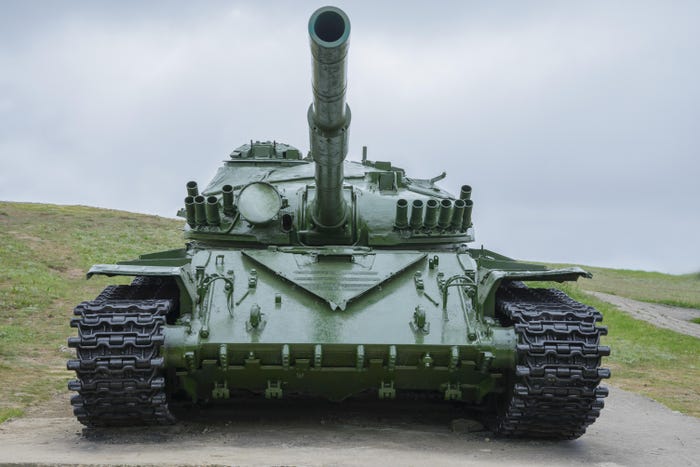
Cyberattacks & Data Breaches
Military Tank Manual, 2017 Zero-Day Anchor Latest Ukraine CyberattackMilitary Tank Manual, 2017 Zero-Day Anchor Latest Ukraine Cyberattack
The targeted operation utilized CVE-2017-8570 as the initial vector and employed a notable custom loader for Cobalt Strike, yet attribution to any known threat actor remains elusive.
Keep up with the latest cybersecurity threats, newly discovered vulnerabilities, data breach information, and emerging trends. Delivered daily or weekly right to your email inbox.






.png?width=100&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)














.jpg?width=100&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)

























