Verizon Mobility Security Index Shows Enterprises Not Doing Enough
The Verizon Mobility Security survey shows enterprises are aware of the growing risk that smartphones and tablets present but aren't doing enough to address it.

Enterprises are aware that growing use of mobile devices in business is increasing security risks, but many of them admit they aren't yet doing all they can to mitigate those risks. This is in part because they are putting other business goals first, according to the first Mobile Security Index conducted by Verizon Wireless Business Group.
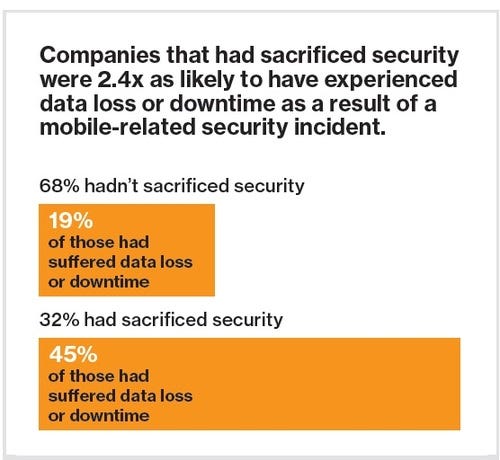
Verizon Wireless surveyed 600 mobility professionals, including many from multi-national corporations, and found that while 93% admitted the growing use of smartphones and tablets is creating greater security risks, almost one third admitted sacrificing mobile security to improve business performance.
That behavior could include things such as using public WiFi networks that aren't secured in order to access business apps -- 14% of those surveyed admitted doing this, even when it is against policy -- notes Justin Blair, executive director of mobile business products for Verizon's Wireless Business Group. The purpose of the Mobile Security Index is to raise awareness of the risks, so they can be properly factored in, he adds in an interview.
"We think many businesses are not really understanding how big the risks are when it comes to mobile security," Blair said. "They need to understand that the minute you go from paper to digital, leveraging a tablet, that tablet is a way into the network. So you need to have device management capability and some level of security on that tablet."
The index showed that companies who did sacrifice security for expediency were almost two-and-a-half times more likely to suffer downtime or data loss.
The survey also show that, for 79% of respondents, the greatest concern around mobile security is disruption of business operations, he adds, and not data loss.
"If you have moved away from paper to go digital, if you are relying upon a smart phone or tablet to do your job now, then if you can't access the stuff you are supposed to access, you can't get your job done," Blair said. "That's what many businesses are most concerned about."
One unsurprising statistic from the Mobile Security Index: 86% of respondents agree employee behavior is the greatest risk. This is true in general where corporate security is concerned, but it is especially true in the mobile space because devices such as smartphones and tablets may travel with the employee, who may download an application or access a site that "unwittingly invites a hacker into the network," Blair said. "In many cases, these devices store critical information or employees need to access critical information like financial data in some of the verticals we serve today. But employees are also used to using these devices as consumers and they may not always be aware of what the risks are."
Verizon intends to use the Mobile Security Index to increase the awareness of security tools that can protect business data and operations today including device enrollment programs it has with Apple, Samsung and Google, mobile device management and mobile threat detection software.
Device enrollment programs allow an enterprise to specifically document the mobile devices it purchases and ensure that they have mobile device management software. The device isn't usable until it passes authentication tests, Blair says.
"Right there you are securing a brand new digital asset before you are allowed to touch the network or put business critical information on it," he comments.
Mobile device management also allows the corporation to control what features and functionality an employee can access on the corporate device, through policies, and prohibit risky things such as accessing unsecured WiFi.
"You can also set up custom application stores so you can manage what applications employees are allowed to download on that device," Blair says. "In many cases, if it is a business specific use, such as a tablet in retail store, you want to completely lock down that device, so only business applications are allowed to be use and an employee couldn't be using it to surf YouTube or Netflix after hours."
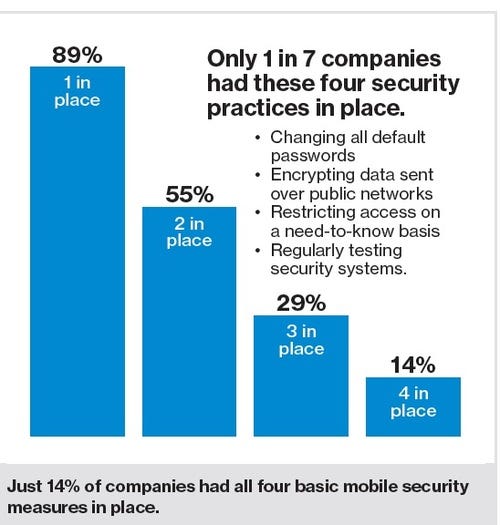
In what has become a sad cliché of many security surveys, this one shows that many businesses who claim to care about security aren't even doing the basics to protect themselves, such as changing default passwords, implementing two-factor authentication or imposing policies that limit riskier behaviors.
"The door is wide open in a few of these areas," Blair says.
— Carol Wilson, Editor-at-Large, Light Reading
Read more about:
Security NowAbout the Author(s)
You May Also Like
Beyond Spam Filters and Firewalls: Preventing Business Email Compromises in the Modern Enterprise
April 30, 2024Key Findings from the State of AppSec Report 2024
May 7, 2024Is AI Identifying Threats to Your Network?
May 14, 2024Where and Why Threat Intelligence Makes Sense for Your Enterprise Security Strategy
May 15, 2024Safeguarding Political Campaigns: Defending Against Mass Phishing Attacks
May 16, 2024
Black Hat USA - August 3-8 - Learn More
August 3, 2024Cybersecurity's Hottest New Technologies: What You Need To Know
March 21, 2024




