Researchers from ICEBEG found malicious code hiding in four popular Google Chrome extensions. The search giant is working to fix the problem.

Google Chrome is the most popular web browser, and four extensions that can inject malicious code into it have been found hiding in plain sight on the Chrome Web Store.
ICEBRG, a US-based security firm, first noticed a problem that included an unusual amount of traffic emulating from a workstation to a European virtual private server (VPS) provider. This caused researchers to dig further, and issue a report on the situation.
What researchers found was a Chrome extension named "Change HTTP Request Header," which could download obfuscated JSON files from the "change-request[.]info" website -- IP address of 109.206.161[.]14 -- via an "update_presets()" function.
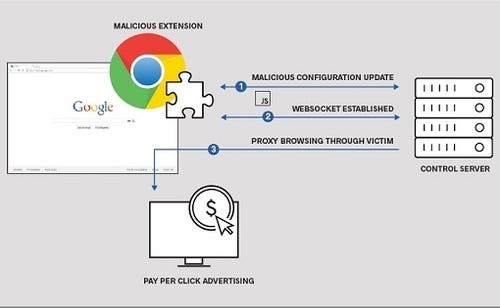
The malicious extension at work
\r\n(Source: ICEBERG)\r\n
Now, Chrome can execute JavaScript code contained within JSON but it's not supposed to be able to do so without explicit permission. The extension snuck in a change in permissions to the browser before the JSON was downloaded and then executed.
The downloaded code was observed by ICEBRG to check for Chrome debugging tools and then halting the execution of the infected segment if those tools were found.
When active, the extension would create a WebSocket tunnel to the command and control server and establish proxy browsing traffic via the victim's browser. It then causes the affected systems to land on advertising sites to which referring sites are paid a "pay per click" bounty. The technique used to make this happen could be used for other malicious actions, however. Browsing the internal network of a victim and bypassing perimeter controls would be one situation that could be easily constructed by use of the same method.
Other Chrome extensions were found to use these same techniques. Specifically, Nyoogle-Custom Logo for Google, Lite Bookmarks and Stickies -- Chrome's Post-it Notes. All of these extensions had a reach of about 500,000 users.
Even though three out of the four extensions had been removed from the Chrome Web Store -- Nyoogle still remains -- they may remain active for unaware users in their browsers.
ICEBRG researchers note that they have notified the relevant parties to "coordinate responses," including the National Cyber Security Centre of The Netherlands (NCSC-NL), the United States Computer Emergency Readiness Team (US-CERT) and the Google Safe Browsing Operations team.
Google seems to be trying to increase extension security on Chrome by limiting code injection of any kind but that may not be practical for all types of software functions.
Google itself will have to come up with a better control mechanism than it currently shows now in order to be a truly enterprise-class browser that cannot be easily fooled.
Related posts:
— Larry Loeb has written for many of the last century's major "dead tree" computer magazines, having been, among other things, a consulting editor for BYTE magazine and senior editor for the launch of WebWeek.
Read more about:
Security NowAbout the Author(s)
You May Also Like
The fuel in the new AI race: Data
April 23, 2024Securing Code in the Age of AI
April 24, 2024Beyond Spam Filters and Firewalls: Preventing Business Email Compromises in the Modern Enterprise
April 30, 2024Key Findings from the State of AppSec Report 2024
May 7, 2024Is AI Identifying Threats to Your Network?
May 14, 2024
Black Hat USA - August 3-8 - Learn More
August 3, 2024Cybersecurity's Hottest New Technologies: What You Need To Know
March 21, 2024




